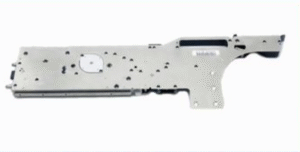
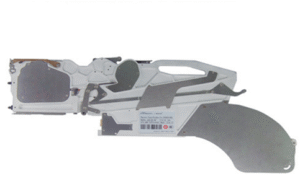
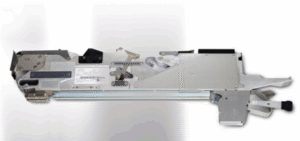

ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR SAMSUNG
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR FUJI
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR PANASONIC
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR YAMAHA
Electric Feeders for SMT: An Introduction to Precision and Intelligence
In the high-speed, high-precision world of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), the placement of components onto a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a ballet of coordinated motion. At the heart of this process lies a critical piece of equipment: the Electric Feeder (also known as a Tape Feeder or E-Feeder). While often overlooked in favor of the flashy pick-and-place machine itself, the electric feeder is a fundamental enabler of modern electronics manufacturing, ensuring that the right component is delivered to the placement head at the exact right moment.
What is an Electric Feeder?
An electric feeder is a motorized peripheral device that mounts directly onto an SMT pick-and-place machine. Its primary function is to store, advance, and present electronic components—such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits—to the machine’s placement head for accurate pickup and placement.
These components are typically supplied on embossed carrier tapes wound into reels. The feeder’s job is to index this tape forward, one pocket at a time, peeling back the protective cover tape to expose the next component for the robotic nozzle.
The Shift from Pneumatic to Electric
Traditionally, SMT feeders were pneumatic, relying on compressed air to actuate their advancing mechanism. While functional, they had significant limitations:
Inconsistency: Susceptible to variations in air pressure.
Noise: Generated high noise levels on the factory floor.
Lack of Feedback: Could not communicate their status or errors to the host machine.
Higher Maintenance: Required regular cleaning and were prone to mechanical wear.
The advent of electric feeders marked a revolutionary step forward. By replacing pneumatic pistons with precise stepper or servo motors, they introduced a new level of control, intelligence, and reliability to the SMT line.
Key Advantages of Electric Feeders
Unmatched Precision and Accuracy:
The digital control of the stepper motor allows for extremely precise tape advancement. This eliminates “component drift” and ensures that each component is presented in the exact same position, every time, leading to higher placement accuracy and fewer mis-picks.
High-Speed Performance:
Electric feeders can operate at much higher speeds than their pneumatic counterparts. Their rapid, controlled movements are essential for keeping pace with today’s ultra-high-speed placement machines, maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Intelligence and Communication:
This is a game-changer. Electric feeders are equipped with microchips that allow them to communicate with the pick-and-place machine.
Automatic Setup: The machine can automatically identify the feeder type and component loaded, drastically reducing setup time and human error.
Real-Time Monitoring: The feeder can report its status (e.g., “Tape Low,” “Cover Tape Jam,” “Feeder Missing”) directly to the machine’s operator.
Data Logging: They can track usage cycles, enabling predictive maintenance.
Reduced Noise and Energy Consumption:
Without the constant “hiss” of compressed air, electric feeders contribute to a much quieter factory environment. They also consume less overall energy, leading to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Enhanced Reliability and Uptime:
With fewer mechanical parts subject to wear and tear and the elimination of air pressure dependencies, electric feeders are inherently more reliable. This translates to less machine downtime and higher production yields.
Applications in Modern SMT Assembly
Electric feeders are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they come in various widths (e.g., 8mm, 12mm, 16mm, 24mm) to accommodate different component sizes. They are indispensable across the entire spectrum of electronics manufacturing:
Consumer Electronics: For smartphones, laptops, and televisions.
Automotive: For advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment.
Medical Devices: For critical, high-reliability equipment.
Industrial and Aerospace: For robust and complex control systems.
Conclusion
The electric feeder is far more than a simple tape-advancing mechanism. It is a sophisticated, intelligent component of the SMT ecosystem that directly impacts production speed, flexibility, and quality. By enabling precision, providing critical data, and ensuring reliable operation, electric feeders have become a cornerstone of efficient, modern, and “smart” SMT manufacturing floors, paving the way for the continued miniaturization and complexity of the electronics we rely on every day.
Share to:




ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR SAMSUNG
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR FUJI
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR PANASONIC
ELECTRIC FEEDER FOR YAMAHA
Electric Feeders for SMT: An Introduction to Precision and Intelligence
In the high-speed, high-precision world of Surface Mount Technology (SMT), the placement of components onto a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a ballet of coordinated motion. At the heart of this process lies a critical piece of equipment: the Electric Feeder (also known as a Tape Feeder or E-Feeder). While often overlooked in favor of the flashy pick-and-place machine itself, the electric feeder is a fundamental enabler of modern electronics manufacturing, ensuring that the right component is delivered to the placement head at the exact right moment.
What is an Electric Feeder?
An electric feeder is a motorized peripheral device that mounts directly onto an SMT pick-and-place machine. Its primary function is to store, advance, and present electronic components—such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits—to the machine’s placement head for accurate pickup and placement.
These components are typically supplied on embossed carrier tapes wound into reels. The feeder’s job is to index this tape forward, one pocket at a time, peeling back the protective cover tape to expose the next component for the robotic nozzle.
The Shift from Pneumatic to Electric
Traditionally, SMT feeders were pneumatic, relying on compressed air to actuate their advancing mechanism. While functional, they had significant limitations:
Inconsistency: Susceptible to variations in air pressure.
Noise: Generated high noise levels on the factory floor.
Lack of Feedback: Could not communicate their status or errors to the host machine.
Higher Maintenance: Required regular cleaning and were prone to mechanical wear.
The advent of electric feeders marked a revolutionary step forward. By replacing pneumatic pistons with precise stepper or servo motors, they introduced a new level of control, intelligence, and reliability to the SMT line.
Key Advantages of Electric Feeders
Unmatched Precision and Accuracy:
The digital control of the stepper motor allows for extremely precise tape advancement. This eliminates “component drift” and ensures that each component is presented in the exact same position, every time, leading to higher placement accuracy and fewer mis-picks.
High-Speed Performance:
Electric feeders can operate at much higher speeds than their pneumatic counterparts. Their rapid, controlled movements are essential for keeping pace with today’s ultra-high-speed placement machines, maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Intelligence and Communication:
This is a game-changer. Electric feeders are equipped with microchips that allow them to communicate with the pick-and-place machine.
Automatic Setup: The machine can automatically identify the feeder type and component loaded, drastically reducing setup time and human error.
Real-Time Monitoring: The feeder can report its status (e.g., “Tape Low,” “Cover Tape Jam,” “Feeder Missing”) directly to the machine’s operator.
Data Logging: They can track usage cycles, enabling predictive maintenance.
Reduced Noise and Energy Consumption:
Without the constant “hiss” of compressed air, electric feeders contribute to a much quieter factory environment. They also consume less overall energy, leading to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Enhanced Reliability and Uptime:
With fewer mechanical parts subject to wear and tear and the elimination of air pressure dependencies, electric feeders are inherently more reliable. This translates to less machine downtime and higher production yields.
Applications in Modern SMT Assembly
Electric feeders are not a one-size-fits-all solution; they come in various widths (e.g., 8mm, 12mm, 16mm, 24mm) to accommodate different component sizes. They are indispensable across the entire spectrum of electronics manufacturing:
Consumer Electronics: For smartphones, laptops, and televisions.
Automotive: For advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment.
Medical Devices: For critical, high-reliability equipment.
Industrial and Aerospace: For robust and complex control systems.
Conclusion
The electric feeder is far more than a simple tape-advancing mechanism. It is a sophisticated, intelligent component of the SMT ecosystem that directly impacts production speed, flexibility, and quality. By enabling precision, providing critical data, and ensuring reliable operation, electric feeders have become a cornerstone of efficient, modern, and “smart” SMT manufacturing floors, paving the way for the continued miniaturization and complexity of the electronics we rely on every day.
LCX Copyright © 2026 All Rights Reserved.